Recombinant Proteins: Production, Applications, and Benefits
Recombinant proteins are genetically engineered proteins produced through genetic modification in host organisms such as bacteria, yeast, mammalian cells, or insect cells. The process involves inserting a gene of interest into a host cell, which then synthesizes the desired protein. This technology is pivotal in biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and medical research.
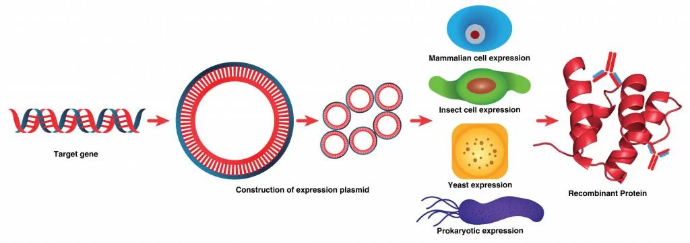
Process of Recombinant Protein Production :
- Gene Cloning: The gene encoding the target protein is inserted into an expression vector, which is then introduced into a host cell.
- Transformation/Transfection: The vector carrying the gene is introduced into host organisms (e.g., E. coli, yeast cells, or mammalian cells) for protein expression.
- Protein Expression: The host cell is cultured to induce the production of recombinant proteins.
- Protein Purification: Recombinant proteins are purified using techniques like affinity chromatography, size-exclusion chromatography, and ion-exchange chromatography.
- Characterization: The purified protein is analyzed for activity, structure, and purity using methods like Western blotting, mass spectrometry, and enzymatic assays.
Applications of Recombinant Proteins :
- Therapeutics:
- Recombinant insulin for diabetes treatment.
- Recombinant growth factors (e.g., erythropoietin) for anemia and human growth hormone for growth disorders.
- Monoclonal antibodies for treating cancer, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases.
- Vaccines:
- Recombinant vaccines like the hepatitis B vaccine and HPV vaccine, created using recombinant technology for disease prevention.
- Diagnostic Tools:
- Recombinant proteins are used as standards in immunoassays such as ELISA, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry for diagnostic testing and biomarker detection.
- Research and Development:
- Protein function studies to explore protein interactions, structure, and biological roles.
- Recombinant enzymes for use in biocatalysis, biosensors, and biofuels production.
- Biopharmaceuticals:
- Large-scale production of therapeutic proteins like blood clotting factors and enzymes for genetic disorders and diseases.
Advantages of Recombinant Protein Technology :
- High Yield: Efficient production of large quantities of protein for clinical use and commercial production.
- Specificity: High purity of recombinant proteins with minimal contaminants.
- Cost-Effective: More affordable compared to traditional methods of protein isolation from natural sources.
- Versatility: Enables the development of targeted therapies, vaccines, and diagnostics.
Recombinant protein technology has revolutionized the fields of biotechnology, biopharmaceuticals, gene therapy, and medical diagnostics, making it a cornerstone of modern medicine and research. Its role in developing innovative drugs, vaccines, and diagnostic tools continues to drive advancements in healthcare and scientific discovery.